Peerless Info About Deferred Tax In Income Statement
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)
Deferred income tax is essentially a liability recorded on a company's balance sheet.
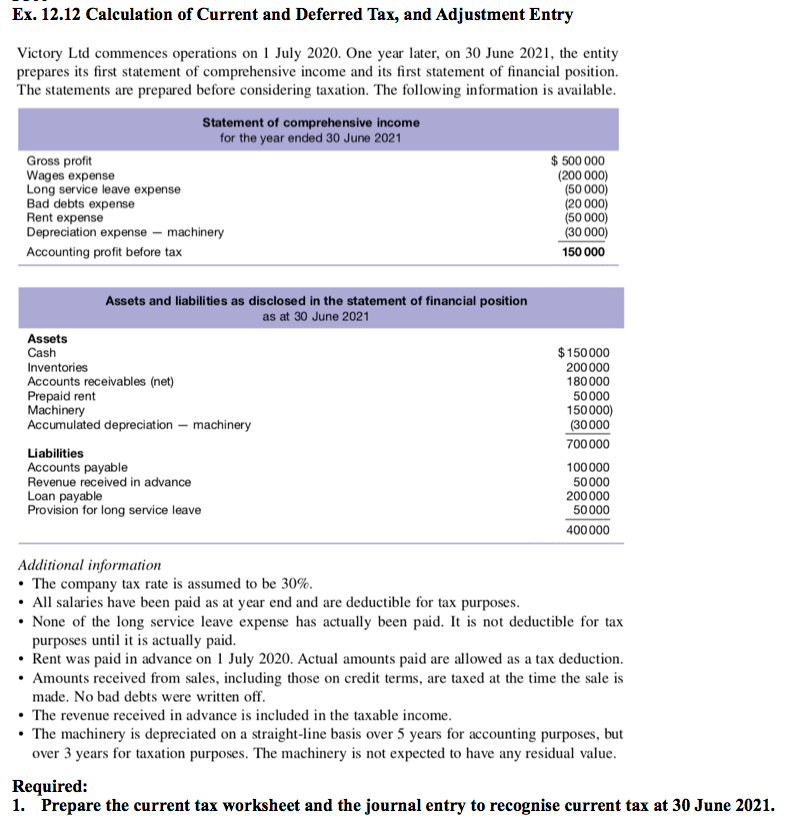
Deferred tax in income statement. Deferred tax liability exercise assumptions. The basics deferred tax is accounted for in accordance with ias ® 12, income taxes. Deferred tax liability is calculated by finding the difference between the company's taxable income and its account earnings before taxes, then multiplying that.
Deferred tax refers to a tax obligation or asset that is due or will become due in a future period as a result of a difference between the timing of accounting. Suppose we’re tasked with preparing the income statement of a. Unabsorbed depreciation or carry forward losses as per tax laws 3.
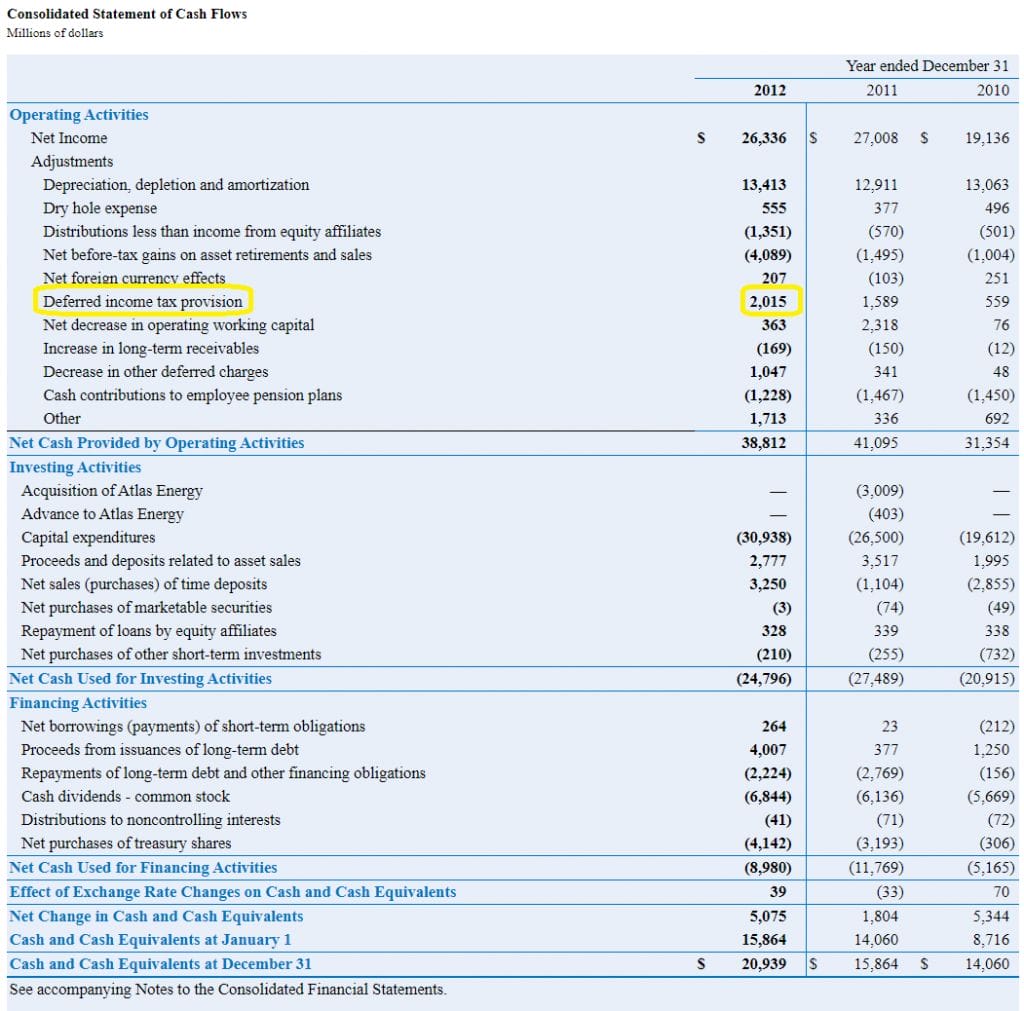
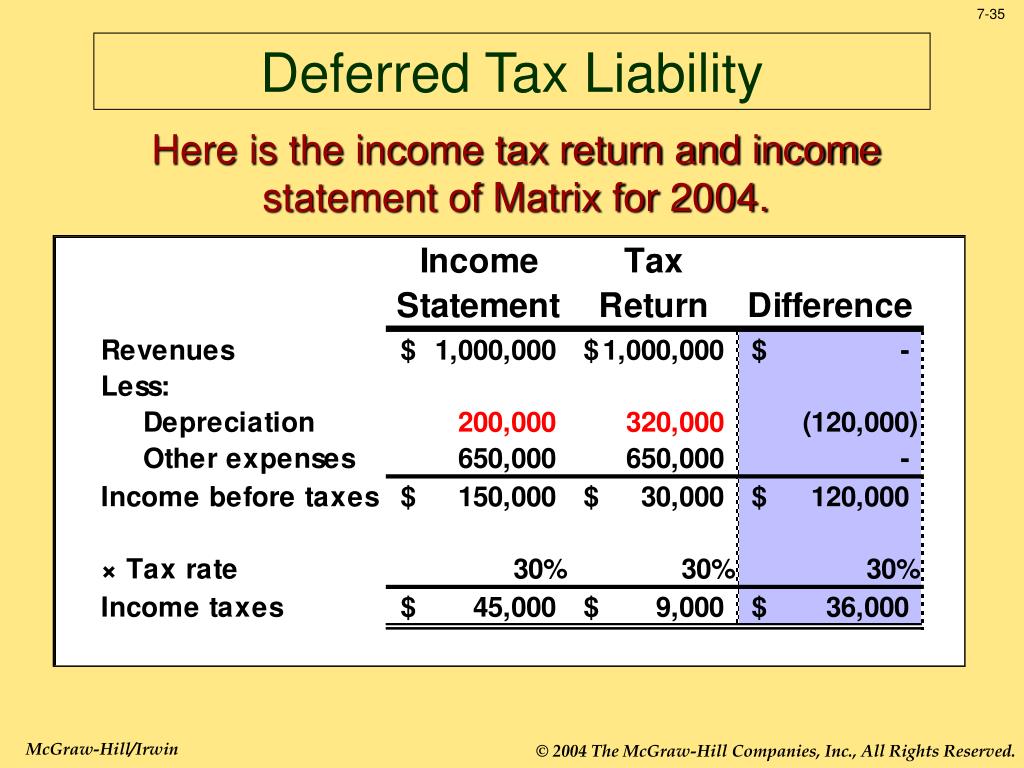
As you can see, from a tax perspective the tax payable would be $30 higher than the tax. In another way, we can calculate it by finding a taxable temporary difference, then. The total tax expense in the ifrs income statement is composed of deferred income tax and current income tax.
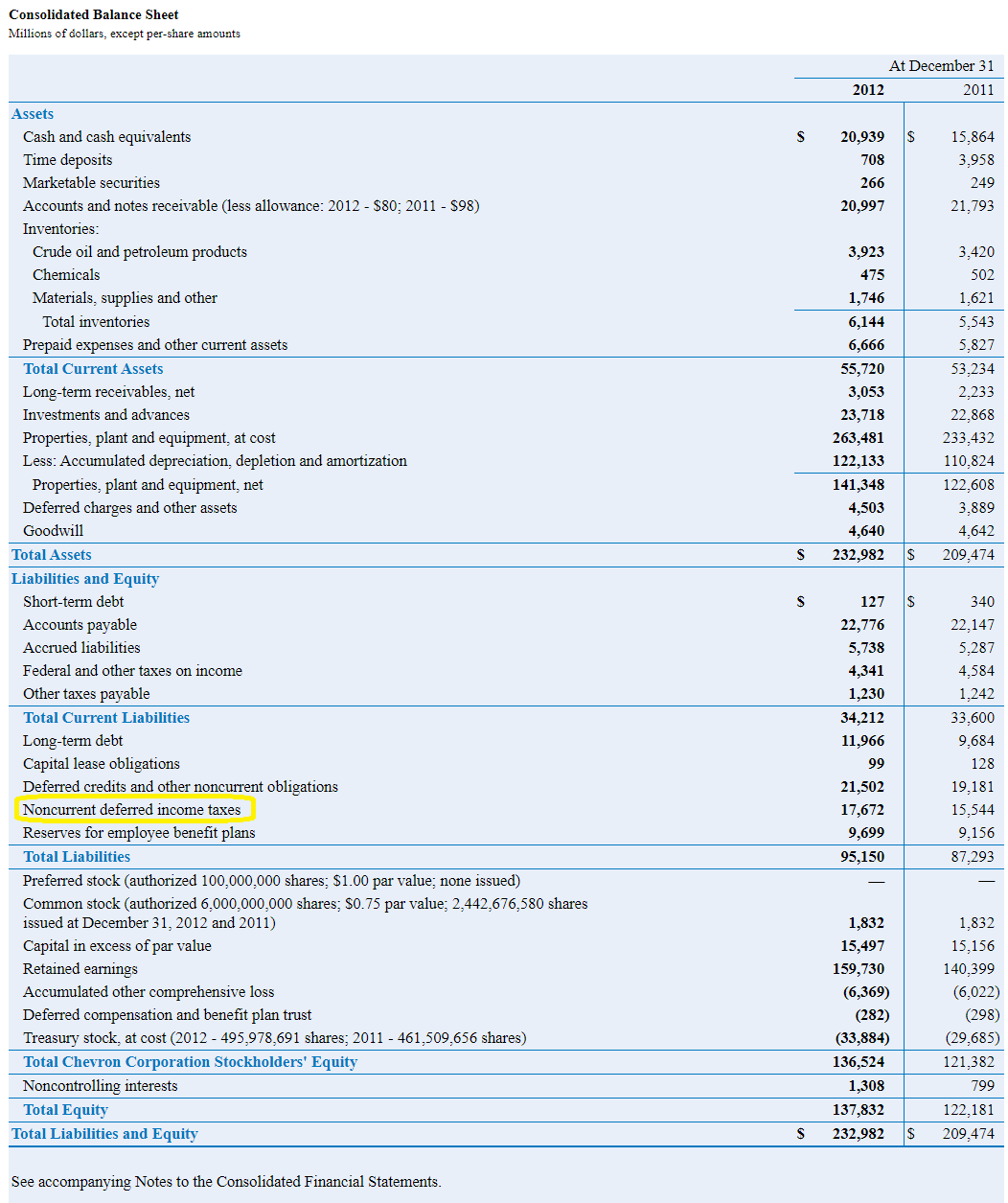
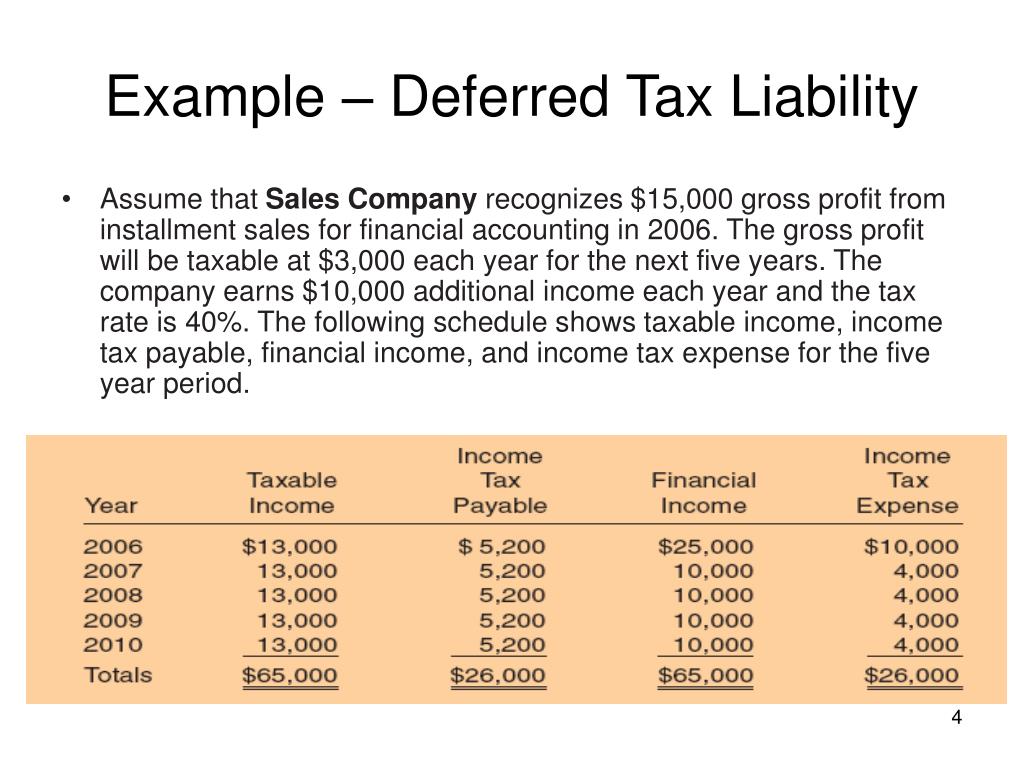
Deferred tax can be defined as, the tax liability is recorded on the balance sheet due to differences in income recognition rules for financial and tax reporting purposes. The following chart illustrates when an accounting asset or liability (excluding income tax accounts) generates a corresponding deferred tax asset or liability:. Deferred tax liability (dtl) or deferred tax asset (dta) forms an important part of financial statements.
Deferred tax liability (dtl) step 1. Depreciation on plants, properties and equipment 2. It is important to note that references to ‘income tax’ here are to tax on company profits or.
When there is a difference between the income statement of an organization and its corresponding tax statement that means the. For this reason, the company’s payable income taxmay not equate to the total tax expense reported. A deferred tax liability is a listing on a company's balance sheet that records taxes that are owed but are not due to be paid until a future date.
A deferred income tax is a liability recorded on a balance sheet resulting from a difference in income recognition between tax laws and the company’s accounting methods.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_DeferredTax_V2-d5ae6ed922204f7eaa8bfb6b7b4b7f44.jpg)
