Best Tips About Equity Balance Sheet Definition
The balance sheet equation, pivotal in financial accounting, posits that the total assets of a company are always equal to the sum of its liabilities and shareholders' equity.
Equity balance sheet definition. Balance sheets provide the basis for. This document gives detailed information about the assets and. Equity is the difference between total assets and total liabilities.
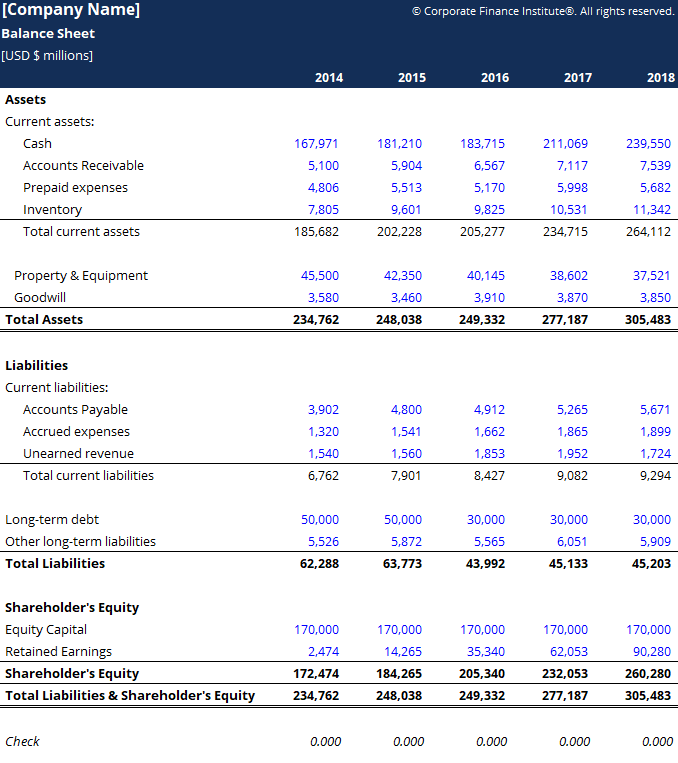
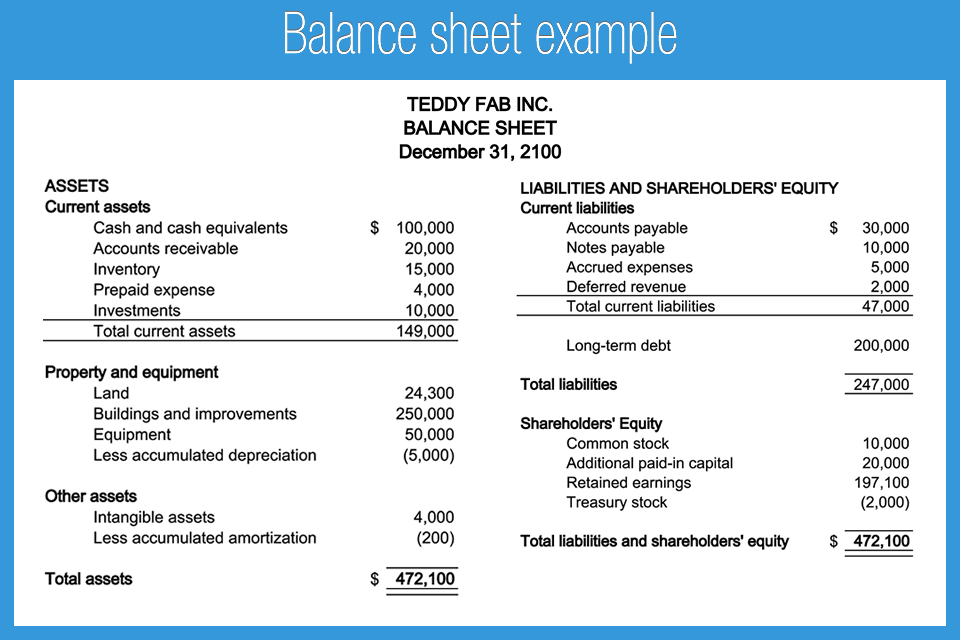
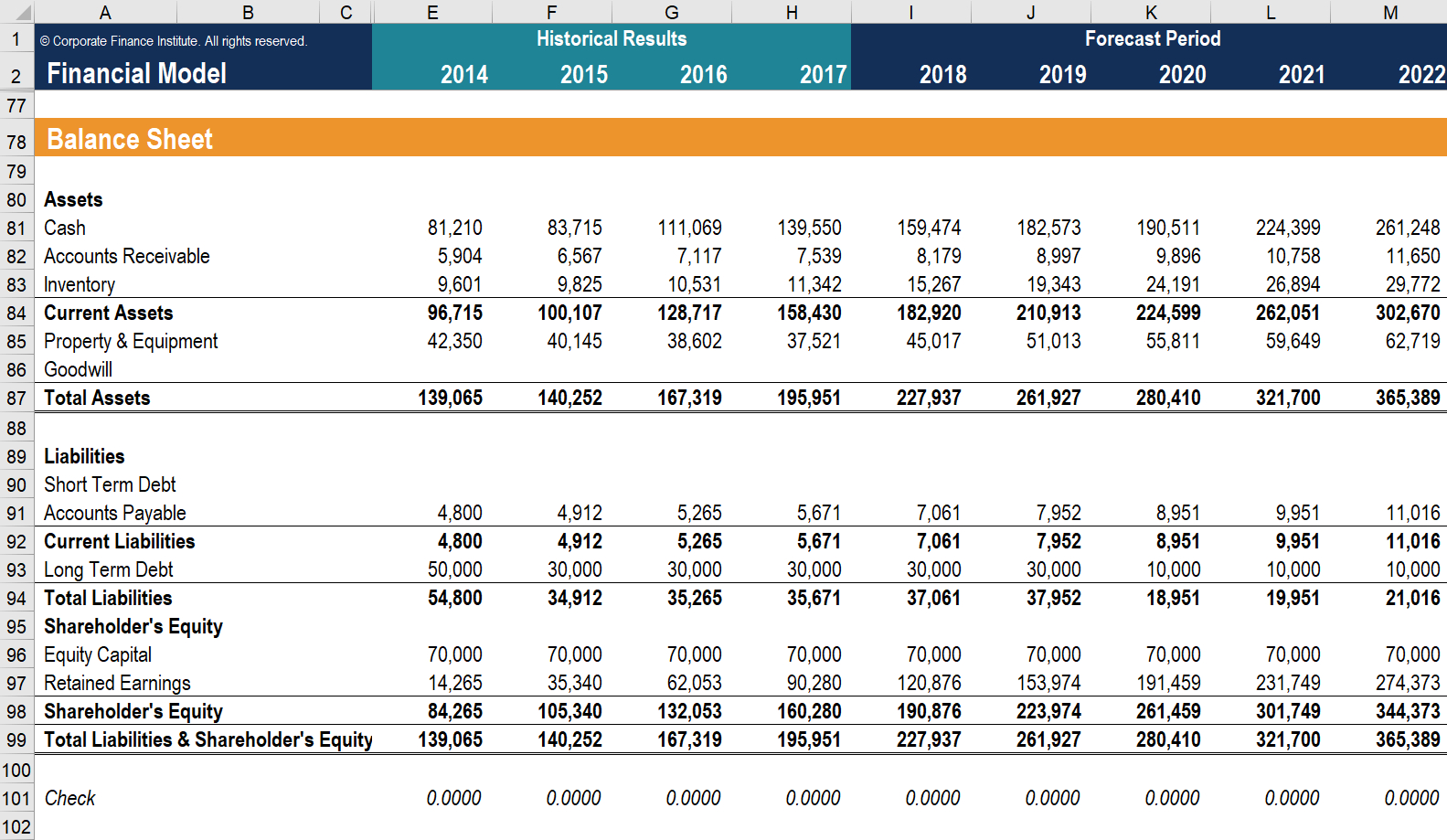
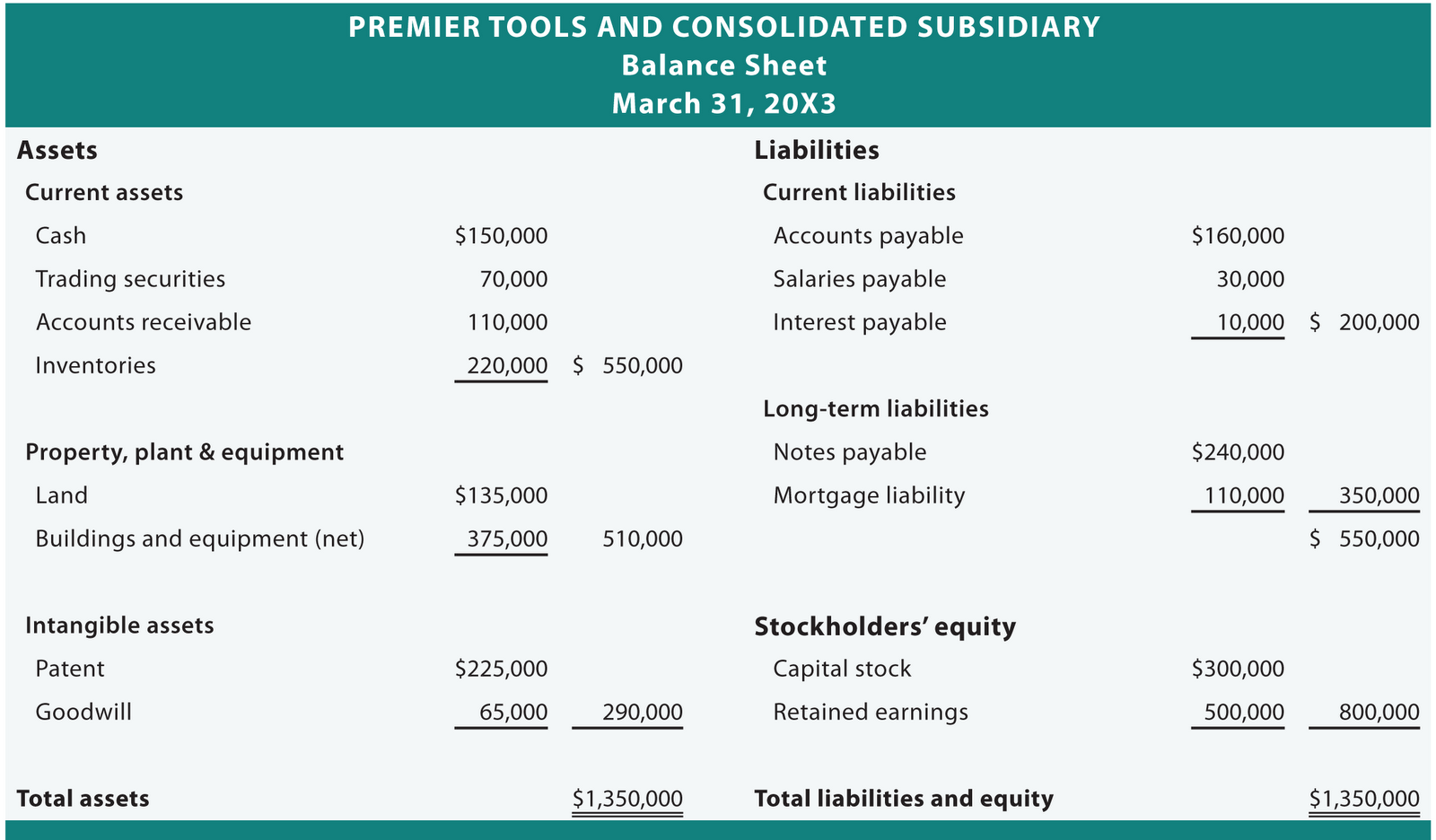
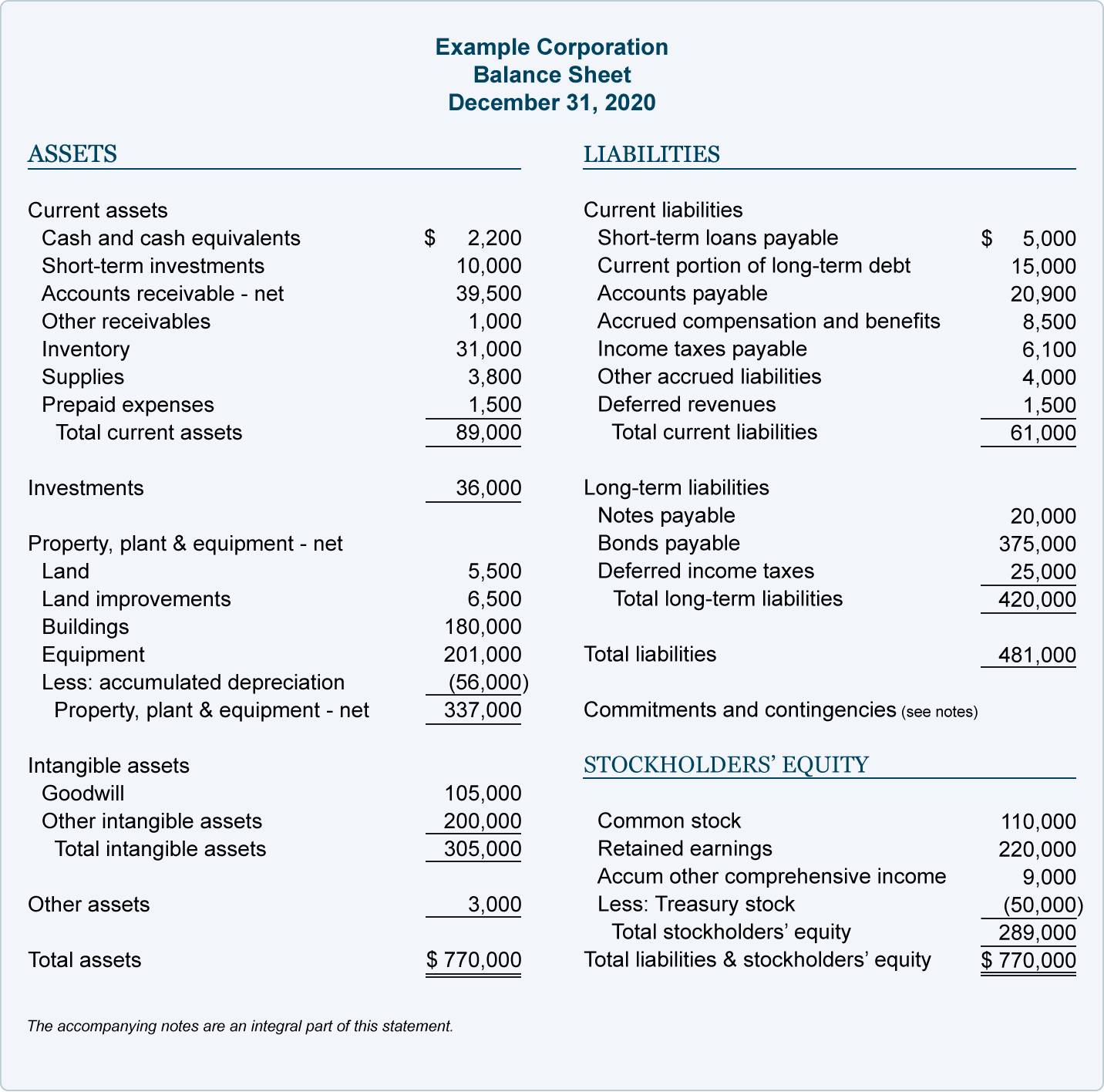
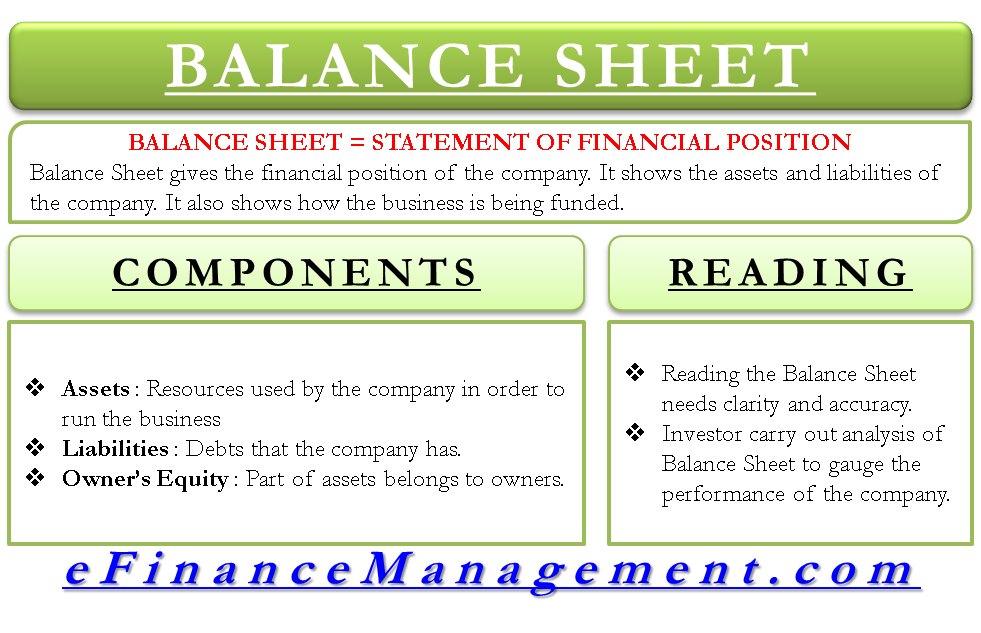
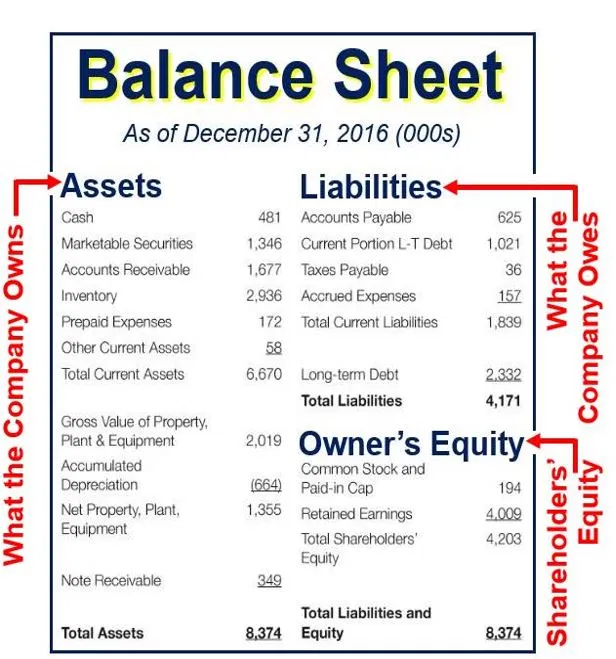
The balance sheet (also referred to as the statement of financial position) discloses what an entity owns (assets) and what it owes (liabilities) at a specific point in time. The total amount of this section is the amount of reported assets minus the amount of reported liabilities. Guides | 4 min read.
In this section, we discuss the significance of recognizing the third equity (entity equity). This study examines whether firms with debt contacts that contain more restrictive balance sheet covenants are more likely to conduct seasoned equity offerings. The term balance sheet refers to a financial statement that reports a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a specific point in time.
The anthony’s (1984) entity theory recognizes entity equity explicitly and classifies the credit side of the balance sheet into three categories, that is, liabilities, shareholders’ equity, and entity equity. While it is sometimes thought of as indicating the value or worth of the business, this is not really the case because assets are listed at their cost value minus accumulated depreciation rather than their actual market value. The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation:
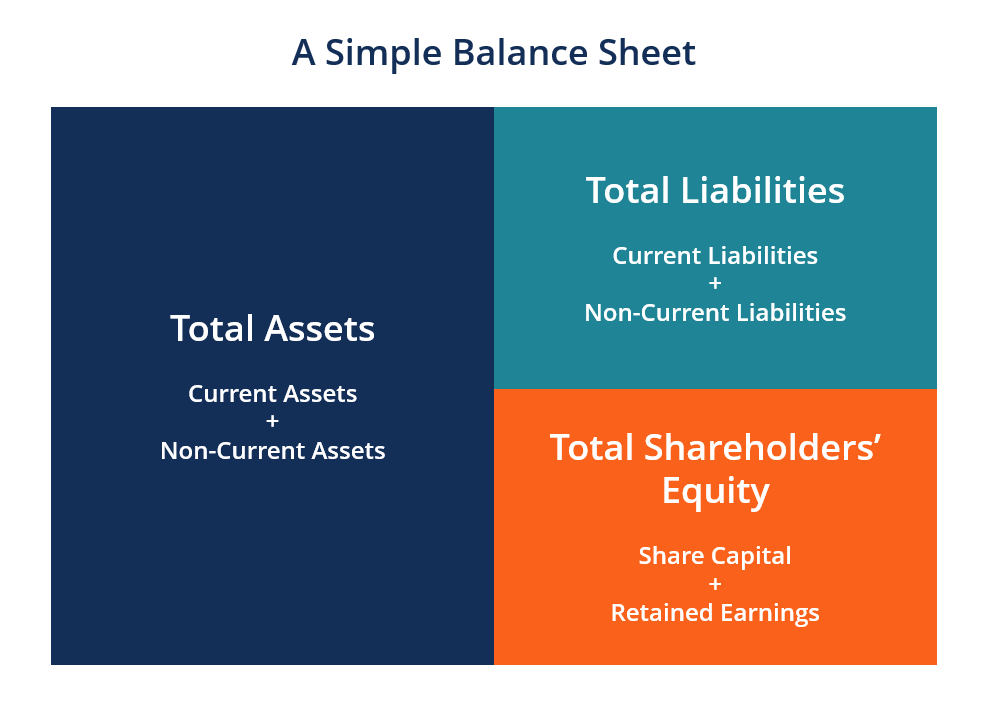
The balance sheet is just a more detailed version of the fundamental accounting equation—also known as the balance sheet formula—which includes assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. All the information needed to compute a company's shareholder equity is available on its. Equity section of the balance sheet definition the part of a balance sheet with the heading stockholders' equity or owner's equity.
The balance sheet displays the company’s total assets and how the assets are financed, either through either debt or equity. The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. In case there is no currency gains/losses or market changes of investments, etc only net profit is included in the equity of balance sheet.
Assets = liabilities + owners’ equity Measuring a company’s net worth, a balance sheet shows what a company owns and how these assets are financed, either through debt or equity. It is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of what a company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested.
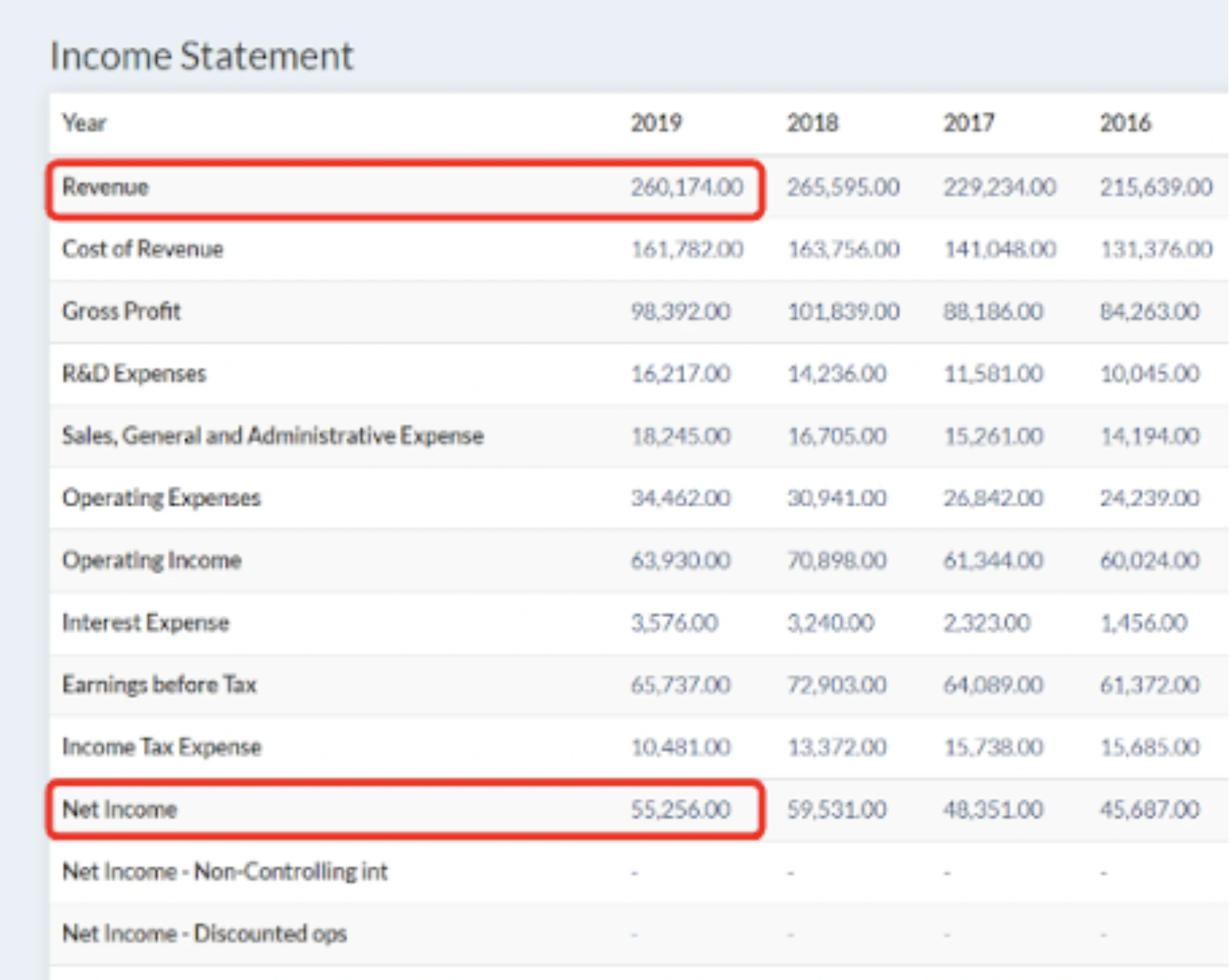
When it comes down to it, the balance sheet is just a more detailed version of the fundamental accounting equation: When the calculation is made, if the result is negative, which happens in case the liabilities are greater than the assets, equity is negative. The book value of equity is calculated as the difference between assets and liabilities on the company’s balance sheet, while the market value of equity is based on the current share price (if public) or a value that is determined by investors or valuation professionals.
Raising capital via equity offerings allows the firm to increase net assets and thereby potentially avoid balance sheet covenant violations. Equity is the owners’ residual interest in the assets of a company, net of its liabilities. Equity in accounting is the remaining value of an owner’s interest in a company after subtracting all liabilities from total assets.
The balance sheet formula is a fundamental accounting equation that mentions that, for a business, the sum of its owner’s equity & the total liabilities is equal to its total assets, i.e., assets = equity + liabilities. A balance sheet is an important reference document for investors and stakeholders for assessing a company’s financial status. The financial statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Equity_Aug_2020-01-b0851dc05b9c4748a4a8284e8e926ba5.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/balancesheet.asp-V1-5c897eae46e0fb0001336607.jpg)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Balance_Sheet_Aug_2020-01-4cad5e9866c247f2b165c4d9d4f7afb7.jpg)
/phpdQXsCD-3c3af916d04a4afaade345b53094231c.png)