Supreme Info About Trial Balance Ppt Ias 12 Deferred Tax Examples

Illustrative examples comparing proposed amendment.
Trial balance ppt ias 12 deferred tax examples. Formulae deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities can be calculated using the following formulae: Ias 12 — income taxes. Other standards have made minor consequential amendments to ias 12.
However, to understand this definition more fully, it is necessary to explain the term ‘taxable temporary differences’. Accrued revenue by an entity, taxable upon cash collection, Recognising a deferred tax liability and increasing the intangible asset’s value.
The following formula can be used in the calculation of deferred taxes arising from unused tax losses or unused tax credits: So, in simple terms, deferred tax is tax that is payable in the future. In this accounting lesson, we explain what deferred tax is, and go through examples of calculating deferred tax.
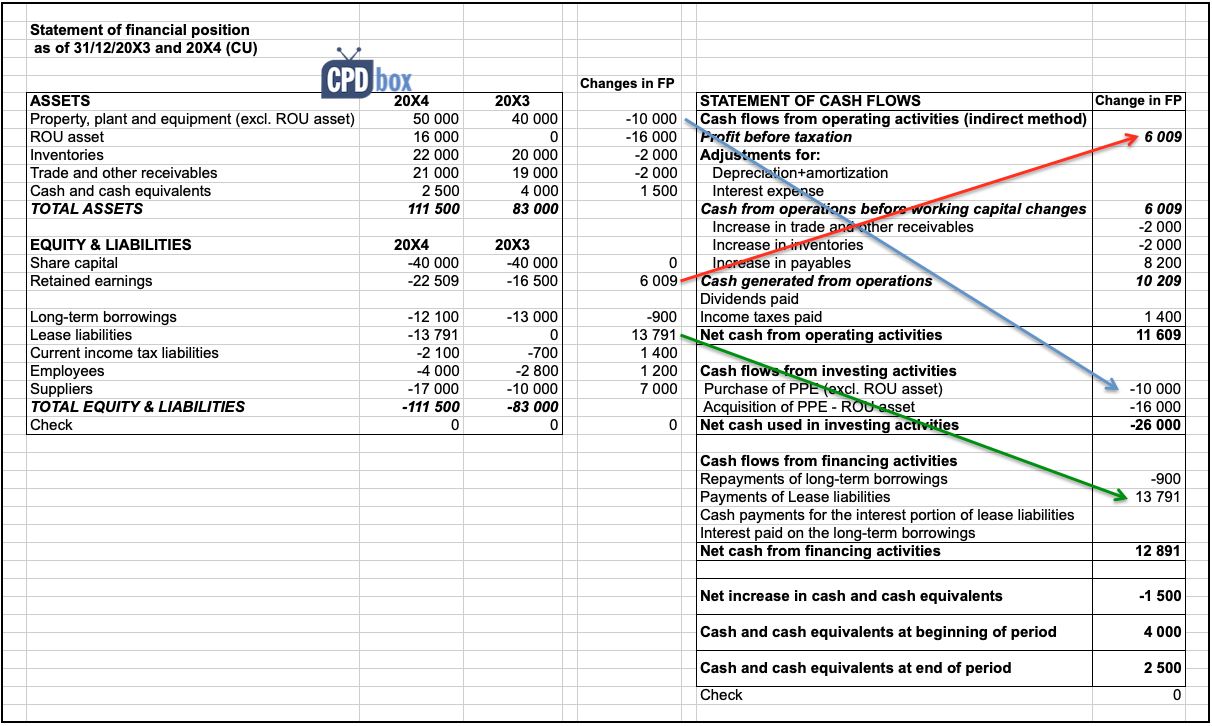
They would also apply to the recognition of decommissioning liabilities and corresponding adjustment to the asset. Pwc examples of temporary differences with deferred tax implications fair valuation of investment property: Background in march 2018 the committee discussed a submission about the recognition of deferred tax when a lessee recognises an asset and liability at the commencement date of a lease applying ifrs 16 leases and whether the initial recognition exemption in ias 12:15 and ias 12:24 would apply to those temporary differences.
Income tax consist of three elements • current tax expense • over/under provision of tax charged the previous period • deferred tax 2/14/2012 mamora abiodun +234802 415 7105 2 Scope of ias 12 this standard deals with in accounting for income taxes and includes all domestic and foreign taxes which are based on taxable profits taxes, such as withholding taxes, which are payable by a subsidiary, associate or joint venture on distributions to the reporting entity deferred taxes this standard does not deal with the. Ias 12 income taxes income taxes ias 12 covers the general principles of accounting for tax.
Amendments to illustrative examples accompanying ias 12 income taxes amendments to the basis for conclusions on ias 12 income taxes from page 4 7 9 10 13 amendments to ias 12 income taxes paragraphs 15, 22 and 24 are amended. In january 2016 the board issued recognition of deferred tax assets for unrealised losses(amendments to ias 12) to clarify the requirements on recognition of deferred tax assets related to debt instruments measured at fair value. Increase in the year (income tax expense) 1,000:
The proposed amendments will typically apply to transactions such as leases for the lessee and decommissioning obligations. Ias 12 defines a deferred tax liability as being the amount of income tax payable in future periods in respect of taxable temporary differences. For assets, the carrying amount of an asset is normally recovered through use, or sale, or use and sale.
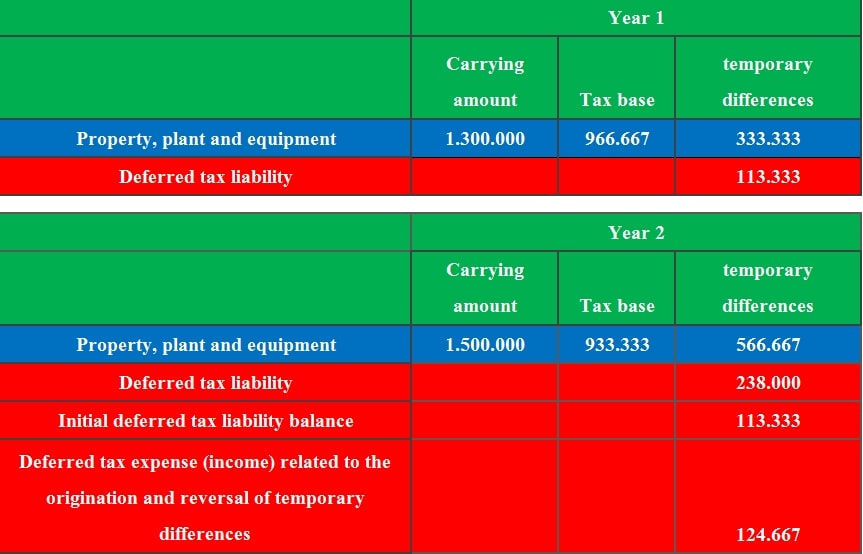
Deferred tax asset = unused tax loss or unused tax credits x tax rate tax bases Increase in the year (income tax expense) 1,000: The iasb has amended ias 12, 'income taxes', to require companies to recognise deferred tax on particular transactions that, on initial recognition, give rise to equal amounts of taxable and deductible temporary differences.
Deferred tax asset = unused tax loss or unused tax credits x tax rate tax bases Deleted text is struck through and. The general principle in ias 12 is that entities should measure deferred tax using the tax bases and tax rates that are consistent with the manner in which the entity expects to recover or settle the carrying amount of the item.
1 deferred tax related to assets and liabilities arising from a single transaction (amendments to ias 12) 2 the amendments have been explained using leases as an example; Tax reconciliation under ias 12 + example by silvia provisions and other liabilities 98 when i was an audit freshman, my least favorite task was to prepare the income tax reconciliation. Opening deferred tax liability: